📌Update for Fetal Echocardiography Mastercourse-
🎯 Learn the art of Fetal Echo from The Best Mentor of the field- Dr. Pradeep Srinivasan
❤️Notes of the sessions will be provided for quick revision❤️
✅It will cover all the topics of Fetal Echocardiography from basics to advance
✅Total 12 sessions, 3hrs each
✅Study material will be provided
✅There will be long access to recorded videos
✅Certificate will be given to participants

.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
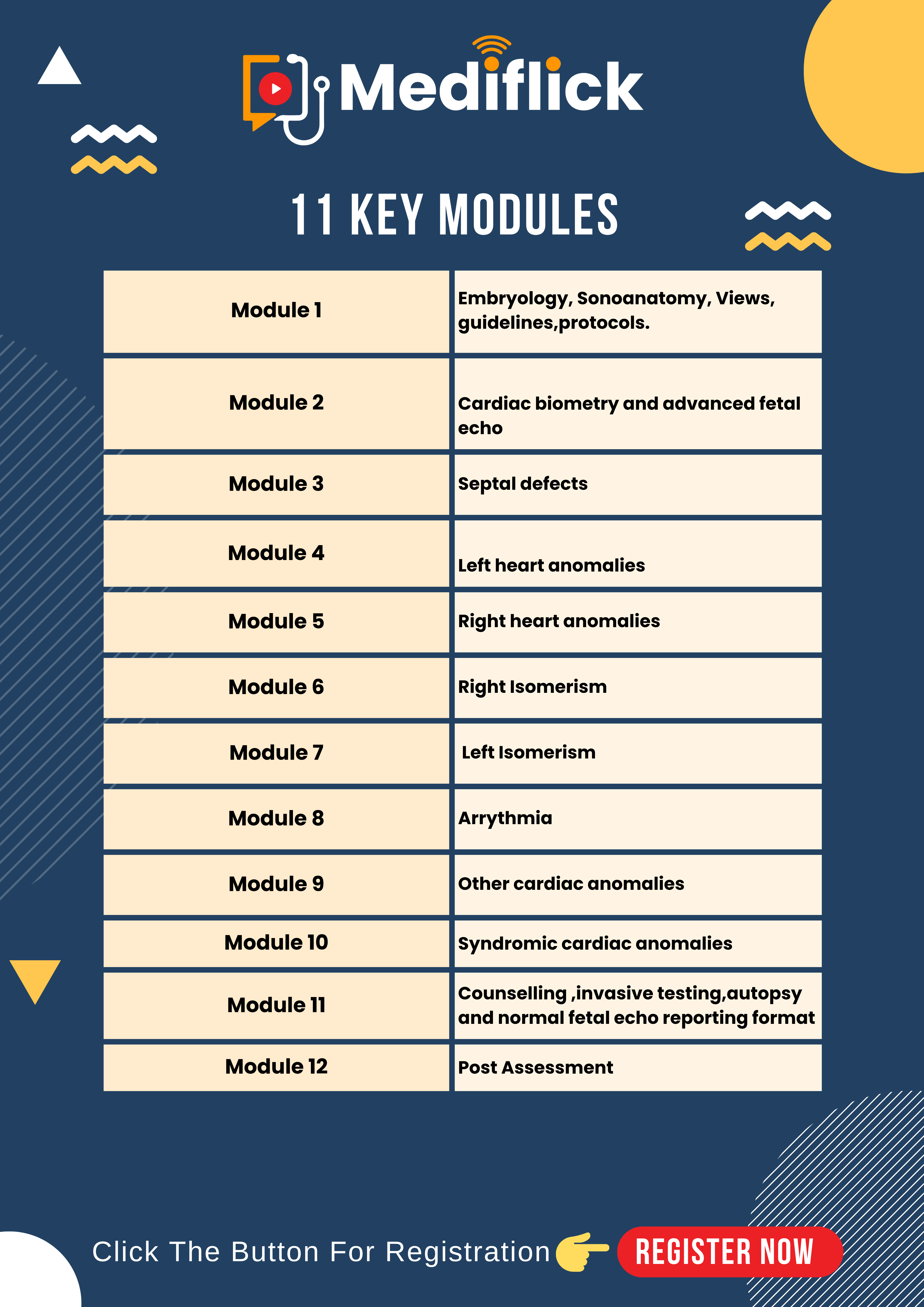
Module 1-
Embryology, Sonoanatomy, Views, Guidelines, Protocols
- Basic embryology needed for radiologist to scan fetal heart is dealt with with explanations and correlations.
- An easy foldable simple cloth made model is used to describe the cardiac formation so that the fusion, rotation, folding etc are realistically understood in a 3D perspective.
- Cardiac chamber anatomy, valve anatomy, inlets, outlets, septae, crux, and relevant anatomy is dealt with in a comprehensive manner.
- Cardiac views with hand probe movements are taught.
- Views in axial, sagittal, coronal sections in 2D, colour doppler, 3D, 4D, 5D are dealt with.
- Doppler across inlets, valves, outlets are dealt with.
- M Mode and its understanding is dealt with.
Protocols
- Protocols of cardiac imaging as per guidelines are dealt with.
- 2D, Colour Doppler, poled wave Doppler, M mode image are used.
- Cine loops of each views in used to five a feel of practical onsite training.
- Pitfalls of imaging are dealt with.
- Knobology and fetal echo settings are taught.
- At the end of this module, one can start practising normal fetal echo views in 2D, colour Doppler and M mode
- The correct machine setting , the correct cardiac zoom, colour optimisation, correct views, ideal Doppler waveforms, M mode trace can be practised.
- Z scores and understanding of basic cardiac biometry will be possible.
Module 2 - Cardiac biometry and advanced fetal ECHO -
- Further to module 1 learning which will make one confidently able to perform fetal echo views in 2D colour and Doppler.
- Module 2 will deal in great detail about various measurements of functional aspects of fetal ECHO
- Measureemnts in 2D views, colour views and measurement in Doppler Waveform and M mode traces are dealt with
- Chamber sizes, outlet sizes, mitral, tricuspid, aortic, pulmonary dopplers, aortomitral dopplers traces are dealt with
- Methods of measurement are taught
- Relationship of cardiac cycle phases with ECG , mitral doppler, aortic Doppler, Aorto mitral Doppler, Pulmonary vein Doppler, IVC Doppler, Ductus venosus Doppler are dealt with.
- Doppler measurements like Peak systolic velocity(PSV), End diastolic velocity (EDV), Systolic/diastolic ( S/D) ratio, Resistance index (RI), Pulsatility Index (PI) ration, time to peak, mean velocity, pre load index are dealt with.
- Ratios like E/A ratio, S/A ratio, etc. are dealt with.
- Myocardial performance index, TEI index, iso volumetric contractions, ejection time, isovolumetric relaxation, ejection fraction are dealt with.
- Z score and importance is dealt with.
- Change of biometry in cardiac failure is dealt with.
- A end of this module, ability to perform advanced chamber size description, stenosis comment, regurgitation assessment, cardiac failure quantification, shunts assessment etc. can be done.
Module 3 - Septal defects -
- After learning basic fetal echo imaging and advanced cardiac biometry, simple congenital cardiac anomalies are dealt here
- Septal defects like atrial septal defects and their types, ventricular septal defects and their types, atrioventricular septal defects and their types are dealt with.
- Definition, etiology, classification, pitfalls, views to demonstrate are dealt with.
- Associated anomalies, extracardiac associations, hemodynamic alterations, complete diagnosis, follow up, counselling, invasive testing are dealt with.
- Multiple cases with static 2D, colour doppler and cine loops are used to shown and explained in each variety to give a virtual onsite learning experience.
Module 4 - Left heart anomalies -
- After learning septal defects, detailed discussion on all types left heart anomalies will be dealt with.
- Anomalies of Mitral valve, Aortic valve, Aortic arch, left Atrium, left ventricle, pulmonary veins, foramen ovale are dealt with.
- Atresia, narrowing, stenosis, hypoplasia , regurgitation, dilatation etc. are dealt with.
- Introduction, classification, etiology, views, alterations, homodynamics, Prognosis, follow up, counselling, invasive testing, autopsy are dealt with.
- Multiple case with 2D, colour Doppler cine loops will be shown to give a virtual on site learning experience.
Module 5 - Right heart anomalies -
- After learning left heart anomalies, focus will be on right heart anomalies.
- Anomalies of SVC, IVC, Right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary artery etc will be dealt with
- Atresia, narrowing, stenosis, absence, dilatation, hypoplasia, abnormal origin, abnormal insertion, regurgitation etc are dealt with
- Introduction, classification, etiology, views, alteration in hemodynamics, prognosis, follow up, counselling, invasive testing, autopsy are dealt with.
- Multiple cases with 2D, colour doppler images and cine loops are shown and explained to give a virtual onsite learning experience.
Module 6 - Right Isomerism -
- After learning simple cases like septal defect, mildly complex bases like left heart anomalies and right heart anomalies and complex cardiac anomalies of right Isomerism or right heterotaxy will be dealt with.
- Normal cardiac and abdominal visceral and vascular anatomy is taught with diagrams.
- Altered right isomerism components with altered cardiac, vascular and visceral anatomy is taught with line diagrams.
- Concepts of situs, like situs solitus, situs invertus , situs ambiguous are dealt with.
- Associated cardiac anomalies, lung anomalies, bronchial anomalies, spine, hepatic, gastric, intestinal, IVC, aortic, azygos vein variations are dealt with.
- Multiple cases with 2D, colour Doppler cine loops with autopsy pictures are shown.
Module 7 - Left isomerism -
- After learning simple anomalies like septal defects, mildly complex anomalies like heart anomalies right heart anomalies and some complex anomalies like right isomerism, another variety namely left heart isomerism is dealt with.
- Normal cardiac, abdominal, visceral, vascular anatomy is taught with line diagrams.
- Concepts of situs, like situs solitus, situs invertus, situs ambiguous, are dealt with.
- Associated cardiac anomalies, lung anomalies, splenic, hepatic, gastric, intestinal, IVC, aortic, azygos veins, variations are dealt with. Conduction anomalies are dealt with.
- Multiple cases with 2D, colour doppler and cine loops with autopsy pictures are shown.
Module 8 – Arrythmia -
- After learning about basics, advanced cardiac biometry, septal defects, left heart anomalies, right heart anomalies, isomerism, etc. Functional rate, rhythm anomalies will be dealt with.
- Introduction to the normal rate, normal rhythm by Doppler and M mode, will be taught.
- Rate, Atrio ventricular time, ventriculo-arterial time and atrio-ventricular conduction, by Doppler and M mode will be dealt.
- Atrio- ventricular trace by Aorto mitral Doppler, SVC Aortic Doppler, pulmonary artery-vein Doppler, etc. will be dealt with.
- Explanations about premature atrial contractions, premature ventricular contraction, supra ventricular tachycardia atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, bradycardia, Blocked Bigeminy , A-V block.
- Long QT syndrome would be addressed.
- Ability to count atrio-ventricular events on M mode will be taught.
- Recognising these different pattern using Doppler and M mode will be taught.
- At the end of this module, one can recognise rhythm anomaly, rate anomaly and classify and diagnose Arrythmia
- Clarification, etiology, diagnosis, treatment, follow up etc. will be dealt with.
Module 9 - Other cardiac anomalies -
- There are a large number of cardiac variations and anomalies which have not been dealt yet are covered in this module.
- Cardiomegaly, cardiac displacements, cardiac malpositions, ectopia cordis, pericardial effusion, cardiac tumors, pericardiac tumors, echogenic intra cardiac focus, myocardial disease, endocardial disease,s, cardiomyopathies, non-compactions etc will be dealt here.
Module 10 - Syndromic cardiac anomalies -
- Fetal Cardiac Syndromes and Associations, Cardiac anomalies associated with chromosomal abnormalities, Syndromic associations and genetic considerations
Module 11 - Counselling ,invasive testing, autopsy and normal fetal echo reporting format
- Multidisciplinary approach to prenatal diagnosis and counselling, (Collaboration with other specialists in maternal and fetal medicine, genetics, and pediatric cardiology for comprehensive care.)
- Ethical Considerations: Discussion of ethical issues related to prenatal diagnosis and fetal interventions.
- Reporting formate of fetal echocardiograms
Module 12 - Post Assessment-
- Time to assess how much you have learnt till now.
Disclaimer: This course is for skill enhancment only. Not valid for PCPNDT registration
Frequently asked question
1. How to Join/ How to access recording of lectures
Ans: After successful purchase, this course will be added to your courses.
You can access Live session/ recording in the following ways:
- From Web browser -
- After successful login, go to the “My courses” Section (just left to the login in the right upper corner) and click the course and watch from there.
- Android / iOS App
- Download the Android / iOS app and after a successful login go to “Library” in the lower bar and click the course and watch from there.
For other devices, you can access courses through the web browser of your device.
Kindly note: Join the Whatsapp group of live course/conference after the registration for better communication and to remain updated.
We also give some special discount for participant of the concern course in future courses, that too updated in whatsapp group and in Email
2. Will the course link be sent to us on E-mail or whatsapp?
Ans: No direct link will be sent to your E-mail or Whatsapp.
Though we will send you reminder Email and Whatsapp message to join the live session.
To get E- mail reminder mark Mediflickinfo@gmail as non-spam, otherwise Email reminder may go to spam folder and you may not be aware of that.
3. I forgot the password to log in on Mediflick.com, what to do?
Ans: Just reset your password. You will get password reset mail. In case you don’t find password reset mail in your inbox, check in spam folder
4. I am unable to log in. I get this message stating I can access only from 10 devices, what to do?
Ans: Log in on every browser or app is considered one device so try to log out from another browser. If issues still persist then kindly Email to us at Mediflickinfo@gmail, we will manually reset no. of devices in 1-2 working days usually.
5. When will I get my certificate of completion of the course/ conference?
Ans: You can manually download your certificate after the completion of the course
For conference, We manually Email certificate after few days of conference
6. When will I get a recording of the live course if available?
Ans: Usually it takes 24-48 hours to access recording after the live course. But in case of any technical issue it may take some longer time. Duration of access to recording is counted after it’s available for participants.
7. I could not complete my course due to some reason, is it possible to get extended access to the recording?
Ans: It’s not possible to extend the recording after it ends. You should purchase a longer duration access option in the course if available or you may have to repurchase the course.
In case of any further question or if you feel any issue kindly write to us and also send us screenshot or video of the issue on Mediflickinfo@gmail.com
Keep Learning
Mediflick.com
Fetal Echocardiography Master Course
Key Highlights
This course covers a systematic approach to fetal heart scanning. The topics range from basics to advanced along with an overview of cardiac genetics and counselling. Early modules cover embryology, Sonoanatomy, Views, Guidelines, Cardiac biometry and scanning protocols. Approach to cardiac defects in detail is covered over various modules, including sequential segmental analysis and abnormal cardiac rhythm. The key topics covered are Septal defects, Left heart anomalies, Right heart anomalies, Right Isomerism, Left Isomerism, Arrhythmia, Other cardiac anomalies, Syndromic cardiac anomalies. The final module covers Counselling, invasive testing, autopsy and normal fetal echo reporting format.
These 12 modules would provide a comprehensive overview of normal fetal cardiac anatomy and scanning techniques, structural anomalies and arrhythmias, common ones being Atrial Septal Defect, Ventricular Septal Defect, Atrioventricular Septal Defect, Ebstein Anomaly, Hypoplastic Right Ventricle, Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome, Univentricular Heart, Tetralogy of Fallot, Truncus Arteriosus, Double-Outlet Right Ventricle, Transposition of Great Arteries, Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return, Coarctation of Aorta, Aortic Stenosis, Pulmonic Stenosis, Cardiosplenic Syndromes, Cardiac Tumors, Cardiomyopathy, Ectopia Cordis, Premature Atrial and Ventricular Contractions, Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Congenital Heart Block.
There will be an post assessment on completion of the course, and qualifiers will be awarded the certificate.
Lecture contents
Module -1 Embryology , sonoanatomy Views guidelines protocols
- Introduction to Fetal Echocardiographyy
- Understanding the fetal heart as a "blinking bonsaai."
- Importance of imaging fetal cardiac structures for early detection of anomalies.
- Basics of cardiac embryology with timeline details.
- Embryology of the Fetal Heart
- Formation of cardiac tubes and their folding, looping, and rotation.
- Development of interatrial, interventricular septa, and AV canals.
- Role of genes like NKX2.5, HAND1, HAND2, and TBX5.
- Critical shunts: ductus venosus, foramen oval, and ductus arteriosus.
- Indications for Fetal Echocardiography
- Maternal factors: diabetic, SLE, teratogens, and IVF.
- Fetal factors: structural anomaly, hydro’s, and rhythm abnormalities.
- Family history and ginetic predispositions.
- Equipment and Settings
- Machine requirements: high-frequency probes, color Doppler, cine loop capability.
- Optimizing image settings: zooom, focus, frame rate, PRF, and harmonics.
- Safety considerations: thermal and mechnical indices.
- Imaging Protocols
- Standard views:
- Axial views: upper abdomen, four-chamber, five-chamber, three-vessel, and three-vessel tracheal views.
- Sagittal and oblique views: LVOT, RVOT, ductal and aortic arches, and bicaval views.
- Doppler applications: atrioventricular, ventriculoarterial, and pulmonary vein Dopplers.
- Detailed View Analysis
- Anatomy and importance of upper abdominal, four-chamber, and five-chamber views.
- 3- vessel and three-vessel tracheal views: PAS alignment and great vessel crisscross.
- RVOT and LVOT views: septo-aortic and metro-aortic continuity.
- Ductal and aortic arches: differences and visualizations.
-
- Practical Considerations
- Guidelines from ISUOG and American Society of Fetal Echocardiography.
- Steps for performing fetal echo in challenging conditions (e.g., high BMI, anterior plecenta).
- Importance of complete scans, even in suboptimal fetal positions.
- Common Anomalies and Their Detection
- Recognizing VSD, ASD, and other conotruncal abnormalities.
- Key views for detecting anomalies based on embryology and flow patterns.
- Learning Aids and Assignments
- Recomended embryology texts for deeper understanding.
- Asignments to practice standard views and Dopler techniques.
Module -2 Cardiac Biometry and Advanced Fetal Echocardiography"
Introduction to Fetal Echocardiography:
-
- Recap of embryology of the heart.
- Basic sonoanatomy and standard imaging protocols.
- Axial and oblique sagittal views in fetal echocardiography.
- Advanced Fetal Echo Techniques:
- Use of cine loops for dynamic visualization.
- Color Doppler for blood flow evaluation across cardiac structures.
- Step-by-step exploration of axial and oblique sagittal views.
- Cardiac Biometry:
- Importance of cardiac measurements for accurate diagnosis.
- Quantification of 2D and Doppler findings for chambers and vessels.
- Z scores and their role in assessing fetal cardiac structures.
- Detailed Imaging Views:
- Axial views: Four-chamber, five-chamber, three-vessel, and three-vessel tracheal views.
- Oblique sagittal views: LVOT, RVOT, ductal arch, aortic arch, and bicaval views.
- Special focus on three-vessel and three-vessel tracheal views for great vessel assessment.
- Doppler Studies:
- Waveform analysis of atrioventricular valves, great vessels, and ductus venosus.
- Understanding ductus venosus S, D, and A waves and their clinical implications.
- Techniques for measuring pulmonary artery, aortic valve, and atrioventricular valves.
- Assessing cardiac rhythms using M mode and Doppler.
- Assessment of Cardiac Function and Anomalies:
- Importance of the E/A ratio in identifying ventricular compliance issues.
- Evaluation of ductus venosus abnormalities, such as deep or reversed A waves.
- Identification of cardiac anomalies, including mesocardia, EIF, and tricuspid valve regurgitation.
- Advanced Biometry and Measurements:
- Chamber and vessel measurements in systole and diastole.
- Integration of Z scores for precise assessment.
- Techniques for PR interval measurement and myocardial performance index (T index).
- Practical Demonstrations:
- Hands-on guidance on obtaining optimal views in challenging fetal positions.
- Practical solutions for common scanning issues, such as Doppler angle correction.
- Interactive Question and Answer Session:
- Clarification of complex concepts, including Z scores, PR interval, and Doppler flow.
- Guidance on clinical relevance and follow-up of findings like EIF and ductus venosus abnormalities.
Module 3 Septal Defects
- Introduction to Septal Defects
- Prevalence and significance in fetal echocardiography
- Types of septal defects and their clinical relevance
- Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD)
- Types of VSD:
- Perimembranous VSD
- Muscular VSD
- Inlet VSD
- Conoseptal (Outlet) VSD
-
- Diagnostic imaging views for VSD:
- Lateral four chamber
- LVOT and short axis views
- VSD-to-aortic dimension ratio for classification of defect size
- Prognosis and surgical indications for VSDs
- Atrial Septal Defects (ASD)
- Embryology of the interatrial septum
- Types of ASD:
- Septum Primum ASD
- Septum Secundum ASD
- Sinus Venosus ASD
- Coronary Sinus ASD
- Flow dynamics and diagnostic imaging approaches
- Associations with genetic syndromes like Down syndrome
- Atrioventricular Septal Defects (AVSD)
- Complete, partial, and intermediate AVSD classifications
- Imaging findings:
- Empty heart sign
- Boomerang sign
- Loss of offset between AV valves
- Associated syndromes (e.g., Trisomy 21)
- Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection (TAPVC)
- Types and diagnostic features
- Associated structural and functional implications
- Left Superior Vena Cava (LSVC)
- Identification and significance
- Associations with chromosomal abnormalities
- Differentiation from TAPVC
- Diagnostic Signs in Septal Defects
- Empty heart sign
- Boomerang sign
- Loss of offset
- Redundant foramen ovale flap
- Dropout artifact
- Crux of the heart and its importance
- Imaging Techniques
- Role of key echocardiographic views:
- Four chamber
- Five chamber
- LVOT
- Short axis
- Optimal Doppler settings and PRF adjustments for flow analysis
- Differentiation of artifacts from true defects
- Genetic and Chromosomal Associations
- Syndromic correlations (e.g., Trisomy 13, 18, 21)
- When to recommend amniocentesis or advanced genetic testing
- Management and Prognosis
- Conservative follow-up for small defects
- Surgical indications for moderate to large defects
- Long-term outcomes for associated anomalies
Module 4 Left Heart Anomalies
1. Introduction to Left Heart Anomalies
- Overview of the wide spectrum of left heart conditions
- Importance of understanding flow-limiting disorders in fetal echocardiography
2. Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS)
- Key diagnostic features:
- Small left ventricle
- Mitral and aortic valve atresia or stenosis
- Enlarged right ventricle
- Associated anomalies:
- Coarctation of the aorta
- Endocardial fibroelastosis
- Trisomy syndromes (13, 18, 21)
- Prognostic considerations and surgical interventions (e.g., Norwood procedure)
3. Aortic Arch Anomalies
- Aortic Arch Interruption:
- Diagnostic imaging findings
- Importance of assessing Z scores and chamber sizes
- Prognostic implications
- Right Aortic Arch:
- U confluence on three-vessel tracheal view
- Association with DiGeorge syndrome
- Bovine Arch:
- Variants in branching patterns
- Distinction from normal aortic arch anatomy
4. Valvular Abnormalities
- Mitral Valve Spectrum:
- Atresia, stenosis, and their effects on left ventricular size
- Aortic Valve Abnormalities:
- Stenosis (valvular, subvalvular, supravalvular)
- Atresia and its role in HLHS development
- Grading of regurgitations (e.g., tricuspid regurgitation)
5. Truncus Arteriosus (Common Arterial Trunk - CAT)
- Single arterial trunk supplying systemic and pulmonary circulations
- Associated findings:
- Truncal valve dysplasia and regurgitation
- Branch pulmonary arteries arising from the truncus
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
6. Diffuse Aortic Calcification (DAC)
- Rare condition with echogenic calcifications in the arterial walls
- Sonographic findings:
- Calcified aortic and pulmonary arteries
- Associated pericardial effusion and polyhydramnios
- Poor prognosis due to associated systemic complications
7. Caudal Regression Syndrome
- Features:
- Absence of sacrum and coccyx
- Imperforate anus
- Bifid scrotum
- Subtle cardiac anomalies such as ventricular size asymmetry
8. Left Ventricular (LV) Aneurysm
- Eccentric outpouching of the LV wall
- Doppler findings:
- Blood filling the aneurysm during ventricular diastole
- Aneurysm contracting with the LV
9. Restrictive Foramen Ovale
- Restricted flow from the right atrium to the left atrium
- Bulging of the fossa ovalis into the left atrium
10. Pulmonary Artery Abnormalities
- Dilated pulmonary artery:
- Potential causes such as left heart anomalies, tricuspid regurgitation, or stenosis
- Importance of Z scores for size assessment
11. Imaging Techniques and Key Doppler Findings
- Use of three-vessel tracheal view, four-chamber view, and cine loops
- Z scores for aorta, pulmonary artery, and chamber sizes
- E/A ratio for mitral and tricuspid valves
12. Genetic and Medicolegal Considerations
- Genetic testing:
- Karyotyping and FISH for 22q11.2 deletion
- Medicolegal implications of missed anomalies:
- Importance of documentation and thorough assessments
Module 5 Right Heart Anomalies
Key Topics Covered in the Lecture:
- Tricuspid Valve Anomalies:
- Tricuspid Atresia
- Tricuspid Valve Dysplasia
- Pulmonary Valve Anomalies:
- Pulmonary Atresia
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome (TOF Variant)
- Ebstein’s Anomaly:
- Displacement of Tricuspid Valve
- Atrialized Right Ventricle
- Double Outlet Right Ventricle (DORV):
- Subaortic VSD
- Subpulmonary VSD (Taussig-Bing Anomaly)
- Doubly Committed and Non-Committed VSD
- Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF):
- Classic TOF
- TOF with Pulmonary Atresia
- TOF with Absent Pulmonary Valve
- Pentalogy of Fallot
- Key Imaging Signs and Techniques:
- Y-Sign in Doppler Imaging
- Ductal Reversal in Severe Pulmonary Obstruction
- Major Aortopulmonary Collateral Arteries (MAPCAs)
- Three-Vessel and Tracheal Views
- Collinearity and Overriding Aorta
- Associated Syndromes and Prognosis:
- 22q11 Deletion and DiGeorge Syndrome
- Chromosomal Abnormalities
- Poor Prognostic Indicators and Duct-Dependent Circulation
Module 6 Right Atrial Isomerism
Topics Covered in the Lecture:
- Introduction to Situs and Isomerism:
- Definitions: Situs solitus, situs inversus, and situs ambiguous.
- The concept of heterotaxy and the distinction between right and left isomerism.
- Embryology of Asymmetry:
- Right-left asymmetry development during embryogenesis.
- Causes and mechanisms leading to isomerism.
- Key Features of Right Atrial Isomerism:
- Bilateral right-sided morphology.
- Asplenia and its clinical implications.
- Central positioning of liver and stomach.
- Malrotation of the gut and associated risks.
- Cardiac Abnormalities:
- Dextrocardia and its significance in right atrial isomerism.
- Common congenital heart defects:
- Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD): Balanced vs. unbalanced.
- Double outlet right ventricle (DORV) and transposition of great arteries (TGA).
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC).
- Mitral and tricuspid regurgitation.
- Hypoplastic right ventricle and truncus arteriosus.
-
- Diagnostic Imaging Techniques:
- Ultrasound and Color Doppler:
- Identifying AVSD, TAPVC, and vascular anomalies.
- Differentiating true ductus venosus reversal from artifact.
- CT Imaging and Contrast Studies:
- Mapping vascular and cardiac abnormalities.
- Gastrography for midgut malrotation.
- Key Diagnostic Signs:
- "Boomerang Sign" and "Empty Heart Sign."
- Vascular relationships, including juxtaposition of aorta and IVC.
- Clinical Cases Discussed:
- Case-based approach to understanding complex presentations of right atrial isomerism.
- Real-world examples highlighting cardiac, abdominal, and systemic anomalies.
- Prognosis and Management:
- Postnatal outcomes and challenges.
- Cardiac surgeries (single vs. biventricular repair).
- Management of associated conditions, such as infections, intestinal malrotation, and respiratory complications.
Module 7 Left Atrial Isomerism
Topics Covered:
- Introduction to Left Atrial Isomerism (LAI)
- Definition and basic anatomy of left atrial isomerism
- Comparison with right isomerism and importance in clinical diagnosis
- Key Diagnostic Features in Left Isomerism
- Visceral Findings: Central or ambiguous liver positioning, right-sided or central stomach, and the double vessel sign with azygos continuation in cases of interrupted IVC
- Cardiac Findings: Commonly associated cardiac abnormalities, including:
- Levocardia, mesocardia, and variations in cardiac orientation
- Atrioventricular Septal Defect (AVSD), DORV, and TAPVC
- Complete heart block and conduction abnormalities
- Pulmonary Features:
- Bilateral bilobed lungs (left lung morphology)
- Bilateral hyparterial bronchi
- Detailed Imaging and Diagnostic Techniques
- Identifying Situs: Determining fetal positioning (cephalic or breech, spine orientation, and labeling left and right for accurate situs identification)
- Aorta-IVC Relationship:
- Typical positioning versus abnormal findings such as piggybacking IVC or double vessel sign indicating interrupted IVC with azygos continuation
- Echocardiography Checklist: Systematic assessment in views such as abdominal, four-chamber, five-chamber, and three-vessel views, along with Doppler imaging to assess blood flow and anatomical structures
- Additional Markers and Signs:
- Atrial and ventricular morphology
- Identification of single vs. double outlets, crisscross great vessels, and offset valves
- Common Anomalies and Their Prognosis
- Polysplenia and Asplenia: Recognizing multiple spleens or absent spleen and their immune implications
- Persistent Left Superior Vena Cava (LSVC): Importance and its effect on the coronary sinus
- Abnormal Stomach and Liver Positions: How to interpret findings of right-sided or centrally located stomach and liver
- Complete Heart Block: High risk in LAI and implications for pacing and long-term care
- Counseling and Risk Assessment
- Guidance on discussing isomerism with patients, explaining the clinical significance of findings, and providing prognostic information based on individual findings
- Explaining sensitivity levels of markers for Down syndrome in a level two scan and how findings like absent nasal bone and echogenic foci influence risk assessment
- Reviewing Case Studies and Practical Imaging Techniques
- Real-time demonstration on how to obtain and interpret essential views such as the lateral four-chamber view for ASD detection, color Doppler for aorta-IVC relationship, and SMA-SMV inversion to assess for gut malrotation
Module 8 Arrhythmia
Lecture Flow and Topics Covered
- Introduction to Fetal Arrhythmia in Echocardiography
- Overview of arrhythmias in fetal echocardiography.
- Complexity and significance of arrhythmia diagnosis in fetal health.
- Basics of Fetal Cardiac Anatomy and Doppler Techniques
- Use of 2D and color Doppler imaging in fetal cardiac assessment.
- Understanding waveforms in atrioventricular and ventricular systolic/diastolic phases.
- Cardiac Biometry and Measurements
- Importance of cardiac biometry in quantifying heart size, flow, rhythm, and velocity.
- Measurements of chamber dimensions, vessel diameters, and Doppler indices for arrhythmia assessment.
- Doppler and M-Mode in Arrhythmia Diagnosis
- Role of Doppler and M-mode imaging in detecting irregular rhythms.
- Techniques for measuring AV and VA intervals and understanding conduction patterns.
- Detailed Classification of Arrhythmias
- Tachyarrhythmias:
- Sinus Tachycardia, Atrioventricular Reentrant Tachycardia (AVRT), Persistent Junctional Reciprocating Tachycardia (PJRT), Atrial Flutter, and Ventricular Tachycardia.
- Diagnostic indicators, Doppler findings, and clinical implications.
- Bradyarrhythmias:
- Sinus Bradycardia, First, Second, and Third Degree Heart Block.
- Differentiation techniques for blocked PACs and heart blocks.
- Factors contributing to poor prognosis.
- Inherited Channelopathies and Associated Conditions
- Overview of channelopathies, including Long QT and Short QT syndromes.
- Diagnostic markers and the genetic predisposition of Long QT syndrome.
- Associated immune and structural conditions: Left atrial isomerism, ccTGA, maternal SSA/SSB antibodies, and myocarditis.
- Practical Diagnostic Algorithm and Doppler Techniques
- Step-by-step approach to identify arrhythmia type and severity.
- Weekly PR interval monitoring and use of steroids and IV immunoglobulin in autoimmune-related heart blocks.
- Management and Treatment Approaches
- Summary of treatment options including digoxin, sotalol, flecainide, and amiodarone.
- Prognostic factors and therapeutic considerations based on arrhythmia type and fetal condition.

.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)